
The Top 10 Must-See Attractions in Gloriando
Introduction to Gloriando and its top attractions Welcome to Gloriando, a hidden gem waiting to…

Introduction to Gloriando and its top attractions Welcome to Gloriando, a hidden gem waiting to be discovered! Nestled in the heart of breathtaking landscapes and rich cultural heritage, Gloriando is a paradise for travelers seeking adventure and relaxation alike. From majestic palaces to serene beaches, this enchanting destination has something for everyone. Join us as…

Welcome to the vibrant world of Pinoyflix, where Filipino entertainment shines bright like a diamond in the vast sea of streaming platforms. From heartwarming dramas to pulse-pounding thrillers, Pinoyflix is a treasure trove of captivating shows that cater to every palate. In this blog post, we will dive deep into the realm of Pinoyflix and…

Are you tired of searching for a reliable online converter to download MP3s from YouTube videos? Look no further! In this blog post, we will explore the world of online converters and compare YTMP3 with other popular tools to see which one truly stands out. Get ready to revolutionize your playlist and unlock the soundtrack…

Introduction to Pinoy Teleseryes Lights, camera, action! The world of Philippine primetime television has been captivated by the melodramatic allure of Pinoy Teleserye. With their gripping storylines, dynamic characters, and emotional rollercoasters, these TV dramas have successfully captured the hearts of Filipino audiences for decades. But what is it about Pinoy Teleseryes that continues to…

Welcome to the exciting world of Fikfap trends, where wellness meets innovation and self-care reaches new heights! In this ever-evolving landscape of health and well-being, staying on top of the latest trends is key to nurturing your mind, body, and soul. Join us as we delve into what’s hot and what’s not in the realm…

Are you tired of searching for the perfect online platform to download your favorite videos and music hassle-free? Look no further, as Y2mate is here to revolutionize your downloading experience! With its user-friendly interface and top-notch features, Y2mate has quickly become a game-changer in the world of online video and music downloads. Let’s dive into…
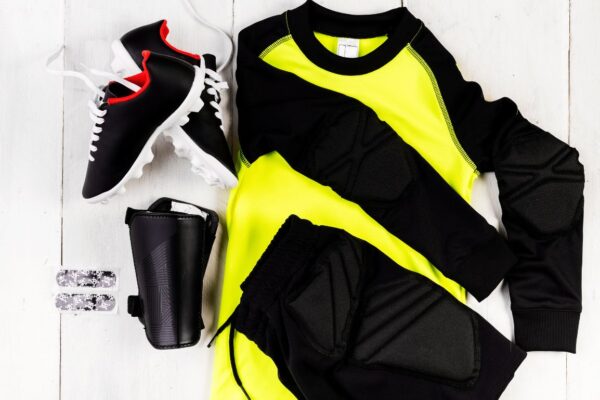

Introduction to Sportsfanfare com Are you a die-hard sports fan looking to show off your team spirit in style? Look no further than SportsFanfare.com – your ultimate destination for all things sports-related! Whether you’re searching for the perfect jersey, rare memorabilia, or unique gifts, this online store has got you covered. Get ready to score…
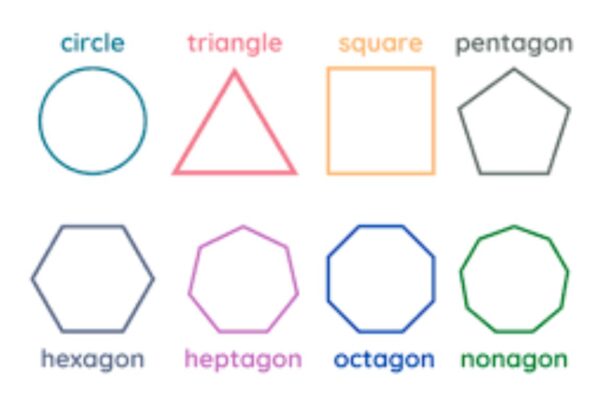
Welcome to a world where shapes come alive, lines intersect with precision, and angles tell a story of symmetry and balance. Today, we embark on a fascinating journey into the realm of geometry – a subject that not only governs the universe’s design but also plays an integral role in our daily lives. Join us…
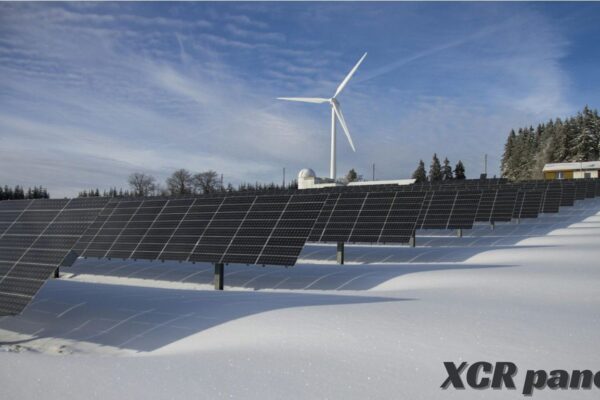

The future of construction materials! In a world where sustainability and eco-friendliness are no longer just buzzwords, but essential factors in building for tomorrow, the XCV Panel is paving the way for a greener, more efficient industry. Join us as we explore how this innovative solution is reshaping the landscape of construction with its cutting-edge…

Introduction to Openhouseperth.net Lawyer and their legal services Are you facing legal challenges and in need of trustworthy guidance? Look no further than Openhouseperth.net lawyer.In the intricate world of law, having a reliable lawyer by your side can make all the difference. Let’s delve into why trusting an Openhouseperth.net Lawyer is essential for your legal…